Bourne Again Shell Command Start a New Bourne again
What is fustigate (Bourne Again Shell)?
Bash (Bourne Again Beat out) is the free and enhanced version of the Bourne crush distributed with Linux and GNU operating systems. Bash is similar to the original, simply has added features such equally command-line editing.
Created to amend on the earlier Bourne shell (named sh), Bash includes features from the Korn shell and the C shell. Bash is intended to conform to the beat standard specified as part of IEEE POSIX. A command language script written for the Bourne shell should too run in the fustigate beat out.
Fustigate is released nether the GNU Full general Public License (GPL), and it is available for almost versions of Unix and Linux and versions have been ported to MS-DOS and Windows.
As explained in the Bash Reference Manual, the name fustigate is an acronym of "Bourne-over again SHell" which is a pun on Stephen Bourne, author of the Bourne beat out. Bash is a superset of the earlier vanquish, and generally compatible with Bourne trounce programs.
What is a shell?
In calculating, a shell plan provides admission to an operating system'southward components. The trounce gives users (or other programs) a way to become "inside" the organization; the shell defines the purlieus between inside and outside.
There are two types of operating system shells:
- Command-line interface (CLI) shells like bash offer users a curtailed and efficient mode of interacting with the OS, without requiring the overhead of a graphic user interface.
- Graphical user interface (GUI) shells, such as Windows and macOS, are considered easier for beginners to use, simply usually also offer programs that emulate a CLI-based shell for system administrators or other ability users who adopt to interact at a command prompt.
Bash is the most ordinarily used CLI shell for Unix-based OSes, including Linux.
What is bash used for?
Bash, like other CLIs, is used for whatsoever computer application that requires precision when working with files and data, especially where large numbers of files or big quantities of data need to be searched, sorted, manipulated or candy in whatsoever way.
Some of the nigh common Bash utilize cases include:
- System administrators utilize Bash to manage systems systematically and reproducibly. System administrators use Bash to troubleshoot systems that are not performance as desired or expected by logging in to systems and reviewing system configurations and network connections. System administrators also rely on Bash scripts to distribute software updates and patches, to monitor running systems, and to update and configure systems.
- Software developers rely on Bash for many development tasks. Bash can exist used to automate software development tasks such as code compilation, debugging source lawmaking, change management and software testing.
- Network engineers use Fustigate to test, configure and optimize network performance on organizational networks.
- Estimator science researchers apply Bash to manage research systems and to deport out enquiry on those systems.
- Hobbyists and ability users use Bash to interact with their systems, execute programs and maintain their systems.
Bash is commonly used interactively, but it can also exist used to write shell scripts. Almost whatsoever computer task can be automated using a Bash script. Bash scripts can exist run on-demand or scheduled to run periodically.
How does fustigate work?
At first sight bash appears to be a uncomplicated command/response system, where users enter commands and bash returns the results after those commands are run. However, bash is besides a programming platform and users are enabled to write programs that accept input and produce output using beat out commands in crush scripts.
One of the most bones bash commands, ls, does i affair: list directory contents. By itself this command lists but the names of files and subdirectories in the current working directory.

The ls control has numerous parameters that modify how the results are displayed. Some often used parameters used with the ls command include:
| ls command-line arguments (parameters) | Purpose |
| -l | Utilize a longer, more detailed, listing format to include file permissions, file possessor, group, size and engagement/time of creation. |
| -a | Listing all files and subdirectories, fifty-fifty those that are usually intended to be hidden. |
| -due south | Display the size of each file. |
| -h | Display file and subdirectory sizes in man-readable format using K, 1000, M and so on to indicate kilobytes, megabytes and gigabytes. |
| -R | Recursive listing of all files and subdirectories under the current working directory. |
Used all together, these parameters give the user a much clearer sense of what files and subdirectories are in a directory, when they take last been changed and past whom.
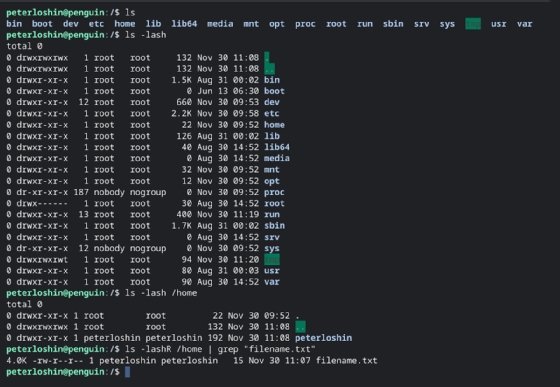
Fustigate enables combining commands by pipage output of 1 command to be used every bit the input for another command. For example, this command can be used to list all files on a file system using the -R parameter to specify the listing should exist recursive:
[email protected]:/$ 1s -1ashR
The response to this command, especially when issued from the arrangement root directory, contains likewise many entries for humans to parse easily. This is where pipes tin come into play, in this case, the user can pipe the output from the ls control to the Bash text design matching command, grep.
The pipe symbol (vertical bar, or "|") directs output from the directory listing into the grep command to render only files and subdirectories with filenames that include the specified text pattern. This command:
[electronic mail protected]:/$ 1s -1ashR |grep 'filename.txt'
returns only files that include the string 'filename.txt' so this command can be used to locate a specific file.
Some things that are much easier to do interactively from the bash control line include:
- file and directory management;
- checking on network configuration;
- editing a configuration file (or any text file); and
- showing the difference between 2 files.
Types of bash commands include:
- Uncomplicated commands, which commonly are run by themselves or with parameters and variables. For example, the ls control takes parameters as well as variables relating to the directories or files to be listed.
- Pipes, which are used to link the output of one or more commands every bit input to other commands.
- Lists, which enable users to run multiple commands in sequence.
- Chemical compound commands, which enable script programming and include loops (for repeating a control a specific number of times) and conditional constructs (for running commands only when a specific condition is met).
Command-line editing is one special fustigate feature not always available with other CLIs. Fustigate retains a command history, which tin can be accessed past pressing the upwardly pointer key. This makes it easier to precisely rerun a command. These prior commands can also be modified at the command line, using special keys to copy, paste, delete or modify a prior command.
Bash is one of the foundations of modern system and network administration, and new users confront a learning curve when using it. However, once learned, bash skills are forever: a time-traveling system ambassador from 1992 would likely be able to become right dorsum to work on a modern Linux system, using fustigate. Learn more about how Fustigate scripting from this tutorial on creating a bash shell that accepts arguments when it runs.
This was last updated in Dec 2021
Continue Reading Well-nigh bash (Bourne once more beat)
- A wait at the main differences of Bourne shell vs. Bash
- Acquire shell scripts: A sys admin's guide to automation
- PowerShell vs. Bash: Key differences for Windows deployments
- Combine PowerShell and Docker to simplify testing beyond OSes
- GNU Bash manual
Dig Deeper on Data center ops, monitoring and management
-

Important DevOps engineer programming languages to acquire
-

batch file
-

command-line interface (CLI)
-

How to script a Bash Shell argument
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchdatacenter/definition/bash-Bourne-Again-Shell



